Table of Contents
In today’s data-driven marketing landscape, simply implementing marketing strategies is no longer enough – you need to understand how these strategies are performing and continuously optimize based on actual data. However, for many beginners, data analysis seems like a complex and mysterious field, filled with technical jargon and complicated tools.

Why is Data Analysis Crucial for Digital Marketing?
Before diving into technical details, let’s understand why data analysis is so important in modern digital marketing:
- Reduce Guesswork, Increase Certainty: Data allows you to make decisions based on facts rather than assumptions
- Optimize Marketing Budget: Understand which channels and strategies deliver the highest returns
- Personalize User Experience: Provide more relevant content and products based on user behavior data
- Predict Future Trends: Identify patterns and trends to anticipate future marketing opportunities
- Prove Marketing Value: Demonstrate concrete results of marketing efforts to management or clients
The Foundation Framework for Digital Marketing Analytics
Successful data analysis isn’t just about collecting numbers, but following a structured process. Here’s a simple yet effective framework:
1. Set Clear Objectives and KPIs
Before you start collecting data, you need to clarify what questions you want to answer and what metrics to measure.
Example Key Questions:
- Which marketing channels bring the highest quality leads?
- How does our content marketing affect conversion rates?
- How many times do users typically interact with our brand before purchasing?
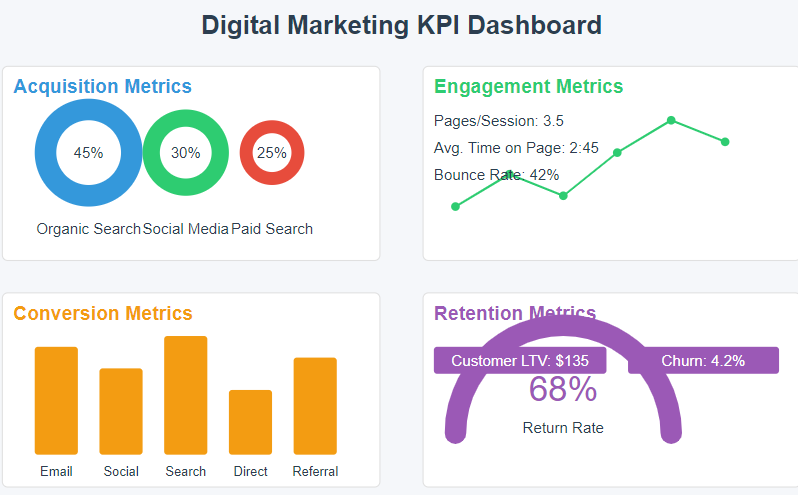
Common KPI Categories:
- Acquisition Metrics: Traffic sources, new visitors, ad click-through rate (CTR)
- Engagement Metrics: Time on page, bounce rate, social interactions
- Conversion Metrics: Conversion rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), leads
- Retention Metrics: Return rate, customer lifetime value (LTV), email unsubscribe rate
2. Set Up Proper Tracking and Data Collection
Once you’ve determined your objectives, you need to ensure you’re collecting the relevant data correctly.
Basic Tracking Setup:
- Google Analytics: Set up goals, events, and e-commerce tracking
- UTM Parameters: Add UTM parameters to all marketing campaigns
- Pixels and Tags: Install Facebook Pixel, LinkedIn Tag, etc.
- Heatmap Tools: Use Hotjar or Crazy Egg to understand user behavior
Learn more about Google Analytics setup
Data Collection Best Practices:
- Create a unified naming convention (especially for UTM parameters)
- Implement data quality checks to ensure accuracy
- Consider privacy regulations (like GDPR, CCPA) compliance requirements
- Regularly audit tracking setups to ensure everything is working properly
3. Analyze and Interpret Data
Collecting data is just the first step; the real value comes from analysis and interpretation.
Basic Analysis Methods:
- Trend Analysis: Observe how metrics change over time
- Segmentation Analysis: Analyze data by channel, device, geography, etc.
- Attribution Analysis: Understand how different touchpoints contribute to conversion
- Cohort Analysis: Compare groups of users acquired during different periods

Avoid Common Analysis Pitfalls:
- Correlation does not equal causation
- Small sample sizes can lead to misleading conclusions
- Focusing too much on short-term fluctuations rather than long-term trends
- Confirmation bias (only looking for data that supports preconceived notions)
4. Turn Insights into Action
The ultimate goal of data analysis is to guide action and improvement.
Action Framework:
- Identify best and worst-performing areas
- Formulate data-based hypotheses explaining why
- Design experiments to test improvement ideas
- Implement changes and monitor results
- Repeat the cycle
Prioritization:
- Focus on high-impact, low-complexity improvement opportunities
- Use the ICE scoring method (Impact, Confidence, Ease) to evaluate potential actions
- Balance short-term wins and long-term strategic improvements
5 Key Marketing Metrics Beginners Must Master
For beginners, the following five metrics provide a solid starting point:
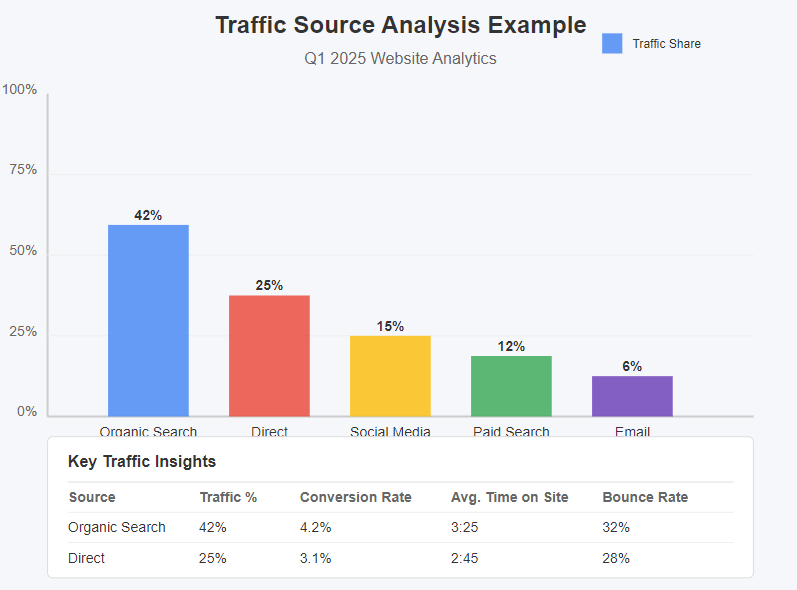
1. Traffic Source Analysis
What It Is: Understanding how visitors find your website (organic search, direct visits, social media, paid ads, etc.).
Why It Matters: Helps you understand which channels are most effective and where you should invest resources.
How to Analyze:
- Look at the “Acquisition” report in Google Analytics
- Compare the quality of traffic from different sources (time on site, bounce rate, conversion rate)
- Identify growth opportunities and declining channels
2. Conversion Rate
What It Is: The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (purchase, sign-up, download, etc.).
Why It Matters: Directly reflects the effectiveness of your website and marketing messaging.
How to Analyze:
- Set up goal tracking in Google Analytics
- Analyze conversion rates by channel, device, and page
- Identify bottlenecks in the conversion funnel
Learn more about conversion rate optimization strategies
3. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
What It Is: The average cost to acquire a new customer.
Why It Matters: Helps evaluate marketing efficiency and sustainability.
How to Analyze:
- Calculate CAC by marketing channel
- Compare CAC to customer lifetime value (LTV)
- Track CAC trends over time
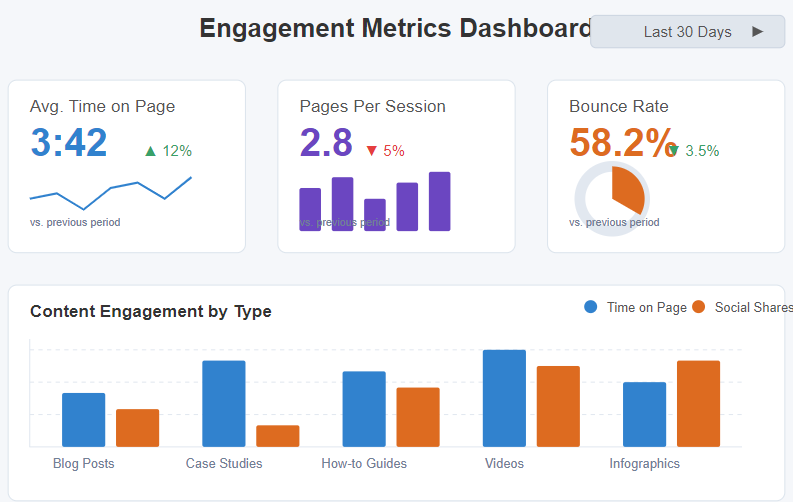
4. Engagement Metrics
What It Is: Metrics that measure how users interact with your content and website (time on page, pages/session, social shares, etc.).
Why It Matters: High engagement often predicts higher conversion likelihood and brand affinity.
How to Analyze:
- Look at the “Behavior” report in Google Analytics
- Identify highest and lowest engaging content
- Analyze user flow and navigation paths
5. Return Rate and Customer Retention
What It Is: The percentage of users who return to your site and the rate at which customers continue to purchase.
Why It Matters: Acquiring new customers typically costs much more than retaining existing ones.
How to Analyze:
- Look at “Audience” > “Behavior” > “New vs Returning” in Google Analytics
- Analyze customer repeat purchase patterns
- Calculate customer churn rate
Explore more customer retention strategies
The Beginner’s Data Analysis Toolkit
Data analysis doesn’t require complex tools. Here are the essential tools beginners should master:
1. Google Analytics
Core Functions:
- Website traffic and user behavior tracking
- Conversion and goal monitoring
- Audience insights
- Custom reporting
Beginner Tips:
- Use the “Home” page for quick overviews
- Set up “Dashboards” to track key metrics
- Leverage “Insights” to automatically discover patterns in data
- Learn to use the “Segments” feature to analyze specific user groups
2. Google Search Console
Core Functions:
- Search performance monitoring
- Keyword insights
- Technical SEO issue identification
- Mobile-friendliness checks
3. Social Media Analytics Tools
Platform Native Tools:
- Facebook Insights
- Twitter Analytics
- LinkedIn Analytics
- Instagram Insights
4. Email Marketing Analytics
Key Metrics:
- Open rate
- Click-through rate
- Conversion rate
- Unsubscribe rate
5. Simple Visualization Tools
Recommended Tools:
- Google Data Studio (free)
- Microsoft Excel/Google Sheets
- Tableau Public (free version)
Data Analysis in Action: 5 Practical Case Studies
Theoretical knowledge needs to be reinforced through practice. Here are 5 practical cases showing how to apply data analysis to common marketing scenarios:
Case 1: Identifying the Most Valuable Traffic Sources
Scenario: An online clothing retailer wants to understand which marketing channels bring the most valuable customers.
Analysis Approach:
- Analyze conversion rates and average order value by source/medium in Google Analytics
- Calculate customer acquisition cost for each channel
- Compare customer lifetime value (LTV) across channels
Findings:
- Organic search had the highest conversion rate (4.2%)
- Instagram ads brought the highest average order value ($85)
- Email marketing had the lowest customer acquisition cost ($12)
Actions:
- Increased investment in SEO, focusing on high-converting keywords
- Adjusted Facebook ad targeting to mirror Instagram audience
- Expanded email list building campaigns
Case 2: Optimizing Content Marketing Strategy
Scenario: A B2B software company wants to improve the marketing effectiveness of its blog.
Analysis Approach:
- Analyze engagement across different content types and topics
- Track content-to-lead conversion paths
- Evaluate content search performance

Findings:
- Case studies had the longest average time on page (4:35)
- How-to guides generated the most leads (8.3% conversion rate)
- Industry trend articles received the most social shares
Actions:
- Created more how-to content
- Added stronger calls-to-action to case studies
- Optimized high-potential but low-ranking content
Case 3: Improving Email Marketing Effectiveness
Scenario: An online course provider wants to improve engagement and conversion rates for its email campaigns.
Analysis Approach:
- Analyze open and click rates across different email types
- Test different sending times and frequencies
- Evaluate the effectiveness of segmentation strategies
Findings:
- Personalized subject lines increased open rates by 35%
- Emails sent Tuesday mornings performed best
- Segmentation based on previous course interests improved click rates by 42%
- Emails containing video had 85% higher conversion rates than text-only
Actions:
- Implemented advanced personalization strategies
- Adjusted sending schedule to prioritize Tuesday and Thursday mornings
- Created more granular audience segments
- Added video content to key promotional emails
Case 4: Optimizing Ad Spend
Scenario: An e-commerce startup wants to maximize returns on its limited advertising budget.
Analysis Approach:
- Analyze ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) by campaign, ad group, and keyword
- Evaluate performance of different bidding strategies and targeting options
- Analyze impact of ad timing and device
Findings:
- Remarketing ads had 3x the ROAS of acquisition ads
- Mobile ads had high click rates but low conversion rates
- Specific interest targeting outperformed broad demographic targeting by 45%
- Ads performed best between 7-10 PM
Actions:
- Reallocated 30% of budget to remarketing campaigns
- Optimized checkout process for mobile users
- Refined interest targeting and reduced broad targeting
- Adjusted ad schedule to increase evening exposure
Case 5: Improving User Retention
Scenario: A subscription-based SaaS app wants to reduce churn and increase customer lifetime value.
Analysis Approach:
- Analyze retention curves across different user cohorts
- Identify behavioral patterns preceding churn
- Evaluate impact of different onboarding and engagement strategies
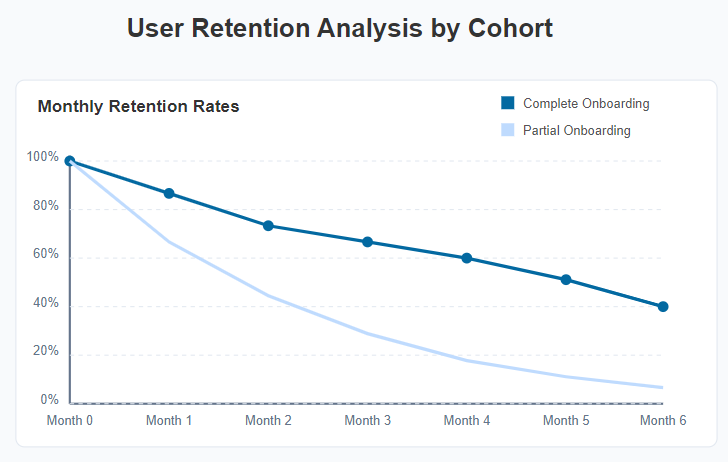
Findings:
- Users who completed the full onboarding process had 60% higher retention
- Users who used the product at least 3 times weekly rarely churned
- Users who contacted customer support in the first month had high churn risk
- Users who utilized specific high-value features had the highest retention
Actions:
- Redesigned onboarding process to increase completion rates
- Implemented incentives to encourage regular usage
- Created proactive support program for new users
- Highlighted high-value features earlier in the user journey
Common Data Analysis Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced marketers make mistakes in data analysis. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
1. Data Silos
Problem: Analyzing data in different systems without getting a complete view.
Solution:
- Implement data integration strategies to bring together data from different sources
- Use analytics platforms that support multi-channel data
- Create cross-channel reports that show the complete user journey
2. Misattribution
Problem: Giving too much credit to last-click or first-click, ignoring the complete customer journey.
Solution:
- Implement multi-channel attribution models
- Consider assisted conversions and attribution windows
- Test different attribution models to understand the impact of various touchpoints
3. Ignoring Statistical Significance
Problem: Drawing conclusions based on too small sample sizes or short timeframes.
Solution:
- Ensure adequate sample sizes (generally at least 100 conversions)
- Use statistical significance tests
- Consider seasonality and external factors
4. Focusing on Vanity Metrics
Problem: Tracking metrics that look good but don’t impact business outcomes (like page views, follower counts).
Solution:
- Distinguish between vanity metrics and impact metrics
- Establish a clear metrics hierarchy connected to business goals
- Focus on metrics that directly impact revenue or customer acquisition
5. Data Overload
Problem: Collecting too much data, leading to analysis paralysis and delayed action.
Solution:
- Start with key questions, not with data
- Create focused dashboards highlighting the most important metrics
- Implement the “So What?” test: each metric should lead to specific actions
Building a Data-Driven Culture: From Individual to Team
Data analysis isn’t just a technical issue but also a cultural one. Here’s how to establish data-driven thinking at both individual and team levels:
Individual Level
- Cultivate Curiosity: Constantly ask “why” and “what if”
- Learn Basic Statistics: Understand correlation, significance, and sample size
- Practice Storytelling Skills: Learn how to tell compelling stories through data
- Develop an Experimental Mindset: View marketing as a series of testable hypotheses
Team Level
- Set Clear Data Goals: Ensure everyone understands key metrics
- Create Shared Dashboards: Make data visible and understandable to everyone
- Regular Data Reviews: Schedule fixed meetings to discuss data insights
- Celebrate Data Wins: Recognize successful decisions made based on data
- Invest in Training: Help team members improve their data literacy

Learning Path for Beginners in Data Analysis
Data analysis is a skill that takes time to master. Here’s a 90-day learning plan:
Days 1-30: Fundamentals
- Learn Google Analytics basics
- Understand key marketing metrics and KPIs
- Set up basic tracking and goals
- Create your first simple dashboard
Recommended Resources:
- Google Analytics Academy free courses
- Google Digital Marketing Fundamentals certification
- “Web Analytics 2.0” by Avinash Kaushik
Days 31-60: Intermediate Skills
- Learn advanced segmentation and filtering
- Understand attribution models
- Start creating reports with Google Data Studio
- Learn A/B testing basics
Recommended Resources:
- CXL’s Conversion Optimization courses
- Google’s Attribution Modeling course
- Optimizely’s A/B testing blog
Days 61-90: Advanced Applications
- Develop custom reports and dashboards
- Learn basics of predictive analytics
- Connect data analysis to business strategy
- Start using APIs for more advanced data
Recommended Resources:
- Data visualization courses on Udemy
- DataCamp’s Introduction to Python for Data Analysis
- “Lean Analytics” by Alistair Croll
Conclusion: Data Analysis is a Journey, Not a Destination
Data analysis isn’t a one-time activity but a continuous cycle of improvement. As you collect more data and gain more insights, your strategies will become more refined and effective.
The key is to start small, focus on metrics that directly impact business goals, and gradually build your analytical capabilities. Remember, the best analysis isn’t the most complex, but the one that leads to clear actions and actual improvements.
By mastering the frameworks and tools introduced in this article, you’ll be able to move beyond guesswork, make evidence-based marketing decisions, and ultimately improve marketing ROI and drive business growth.
You might also be interested in these:
5 Best Email Marketing Tools for Beginners in 2025: A Comprehensive Comparison
5 Best Social Media Management Tools for Beginners in 2025: A Comprehensive Comparison
5 Best AI Content Tools for Digital Marketing Beginners in 2025: Complete Guide
10 Essential Free Digital Marketing Courses to Learn in 2025 | Complete Guide